Summary
Introduction
Education in Vietnam still plays a central role in Vietnamese culture and society. It is considered the path to advancement and families regularly sacrifice a lot to ensure that their offspring receive the required education.
The main goal of education in Vietnam is “to improve people’s general knowledge, train quality human resources, nurture and encourage talents”. In response to public opinion, the Ministry of Education and Training has introduced resolutions to reform the education system, it is trying to overcome outdated curricula and teacher-oriented courses. Although there is still plenty of work to be done, the standards have improved over the years. According to UNESCO statistics, in 2019, more than 95% of Vietnam’s population is literate.
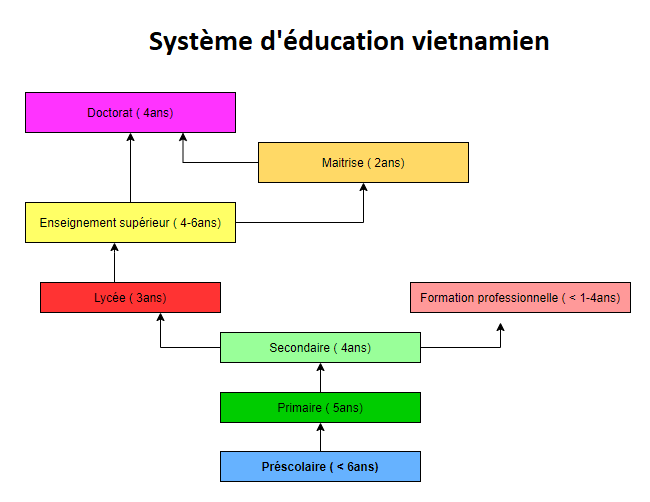
Education in Vietnam is a public and private education system run by the Ministry of Education and Training. The system is divided into five levels:
– preschool (from 18 months)
– primary (from 6 years old)
– secondary (from 12 years old)
– high school (from 16 years old)
– higher education
Formal education includes twelve years of basic education. Indeed, basic education includes five years of primary education, four years of secondary education and three years of high school education.
Besides, there are still interesting things to know about Vietnamese education, such as extracurricular activities, timetables, school discipline and fees.
General information on academic life
Vietnam’s formal education consists of twelve years of compulsory basic education: five years of primary education (from age 6), four years of intermediate education (from age 12) and three years of secondary education (16 years).
It should be noted that kindergarten is not compulsory in Vietnam. We will give more details further down in the article.
To graduate from high school, students must pass the intermediate school-leaving examination. This exam is organized by the local Ministry of Education and Training.
Vietnamese usually have classes Monday through Saturday for 6-8 hours a day in classes of 35-50 students.
It should be noted that education in Vietnam is evolving, previously, lessons were given unilaterally: The teacher gave the lesson and the student listened and wrote. Today, communication and participation are privileged; students work more in small groups.

Vietnam’s education system in detail
Do you want to know more about the Vietnamese education system? In this article, we will show you the fundamental components of the education system in Vietnam to give you a general understanding.
A Vietnamese educational system is organized by the Ministry of Education and Training and applied throughout the country. According to UNESCO statistics, as of 2009, more than 90% of Vietnam’s population is literate.
Now, let’s take a look at the components of the education system in Vietnam.
I. Preschool (kindergarten)
Before the age of 6, it is not compulsory to go to school in Vietnam. You can choose to let your children go to school or stay home at this point.
The nursery, kindergarten: it is a place to look after children when their parents go to work to earn a living. A child can go to kindergarten at the age of 18 months.
Kindergarten: When the child reaches the age of 3, the parents take him/her to the kindergarten where he/she is supposed to familiarize himself with the school from 8:00 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. from Monday to Friday. This routine will continue until the child reaches 5 years old. At this stage, kindergarten teachers will teach children to sing, dance, draw and do some simple activities on their own. Teachers also teach children simple letters and math. Nowadays, since English is becoming more and more popular, English is also added as a subject in kindergarten. Children will learn to familiarize themselves with certain phrases, colors, numbers, shapes, etc. of the most simple and popular form.
II. Primary school – enter General education
When the child is 6 years old, it’s time to officially go to school. A conventional general education class consists of approximately 30 to 40 students. The class often accompanies a class monitor, 2 to 3 sub-monitors, and a homeroom teacher. Students wear school uniforms. The uniform design differs for each school. Generally, the normal course is to spend twelve years for general studies from grades 1 to 12, including primary, secondary, and secondary school, before studying higher education or vocational training.
1. Elementary school
Primary school lasts 5 years, from the 1st to the 5th year. In primary school, students will study literature, mathematics, history, geography, etc. which are taught by a teacher called a head teacher. Other teachers teach other subjects such as art, music, physical education, etc. Pupils who finish primary school go on to secondary school. There is no entrance exam to go to secondary school.
2. High school
Secondary school lasts 4 years, from grades 6 to 9 (children are aged between 12 and 16). A big difference between a primary school and a secondary school is that different teachers teach different subjects. One of the teachers will be the main teacher. In addition to teaching, the main teacher is responsible for supporting students in other aspects such as administrative or consulting tasks. When students finish high school, an exam will be held all over Vietnam to assess student’s skills, which is the high school entrance exam. This entrance exam is currently applied to public and private schools.
At this stage, it is possible to stop general training and start working. The work will then be mostly manual, difficult and not very well paid. Cases of discontinuation of studies in secondary school are often due to a difficult family environment which pushes the student to go to work to bring money into the family.
3. High school
High school lasts 3 years, from 10th to 12th grade (ends at about age 19). In high school, subjects like art and music are eliminated. Students will be responsible for directing their careers and will focus on the subject in which they specialize. When students finish high school, they will have to take a school-leaving exam. This exam will allow access to public and private universities. Regarding this exam, students will choose the specialty they wish to study at the university and take the exams associated with it. In recent years, many changes have been made to this exam regarding the exam form, questions, structures, quizzes, etc.
If the student passes the exam with a mark according to the criterion of the Ministry of Training and Education in Vietnam, he should obtain a diploma considered as the baccalaureate in France.
After high school, you can either go to university, do vocational training, or work.
III. Vocational training
In the educational system of Vietnam, vocational training is designed to teach the student a particular job such as carpenter, hairdresser, tailor,etc. Students after completing their vocational training should have the basic skills for a job. Then he/she can work with an experienced senior to hone their skills, or they can start their own business. This training is divided into two types: short-term training and long-term training. Short-term training lasts less than a year while long-term training lasts 1 to 3 years.
IV. Higher Education
Higher education includes bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral degrees. University training often lasts 4 years in Vietnam, depending on the subject of study. However, for some specific majors such as medical studies, the bachelor’s degree could last 6 years and more. After completing higher education, students can choose to formally enter the labor market or study further. Students often have to spend 2 years for a master’s degree and 4 years for a doctorate.
V. Continuing Education
Moreover, these centers are created with the aim of providing education to all walks of life. If your studies stop unexpectedly for some reason, you can enroll in a course aimed at eliminating the illiteracy rate in society, to encourage people to study when they are ready to do so.
EXTRACURRICULAR ACTIVITY
Speaking of extracurricular activities, students are not used to participating in them. It is better for teachers or parents to encourage students to get involved in other activities outside of school, including student clubs, sports projects and volunteer work. However, as life becomes more modern and requires the necessary outdoor activities for people, extracurricular activities are increasingly responded to by the students themselves.
Schedule and discipline at school
DISCIPLINE
Teachers are highly respected. Indeed, when a teacher enters the classroom, the whole class must stand up to greet the teacher. During class, students pay close attention to the lessons. And at the end of class, students wait until the teachers have to leave the classrooms before they start to leave.
There are specific dress codes regarding clothing and hairstyles. There is a note dedicated to ethical behavior in high school. Many schools require students to wear a uniform and follow a code of conduct. If the rules are broken, there is a school ethics commission. This commission determines the punishment and students are not allowed to earn an average ethical diploma. Romantic relationships are not allowed in school, as they are encouraged to focus on their studies.

Schedule
In Vietnam, a school day starts from 7 am to 11 am and from 1 pm to 4 pm or 5 pm in the afternoon, Monday to Friday and Saturday morning for some schools. Students will also have a 30-minute break in the morning and afternoon. A school year often begins in September and ends in May of the following year.

During a school year, there are holidays on which students are allowed to take one or more days off. Such as Tet vacation, Independence Day, Labor Day, King Hung Memorial Day and Teachers’ Day. Summer often lasts for 3 months from the wait of June to the end of August. However, in recent years, a school year must start earlier in August, which explains why the other vacations of the year will last longer. Summer schools and additional courses such as evening classes are optional. They have been discouraged by the government in recent years.
A school year in Vietnam is often divided into two semesters. There will be a test in the middle and at the end of the semester. The purpose is to test the students’ processes and determine if they are eligible to study in the next class. In the last 3 years, the Minister of Education and Training has implemented a new evaluation system in the elementary school. In particular, teachers will write comments for students instead of grading them. This is intended to reduce the pressure of studying for primary school students. Nevertheless, this system still needs to be improved for better results.
School costs
As far as public schools are concerned, primary school students are exempt from paying school fees. This is to motivate children to go to school and be literate, to be able to do simple mathematics after finishing 5 years of elementary school. In Vietnam’s education system, elementary school is compulsory. Students in other levels of education have to pay about VND 100,000 to VND 200,000 per month for tuition and a little more for other kinds of fees such as lunch, facility fees, etc.
- Nursery: 200 000 VND / month
- Kindergarten: 160 000 VND / month
- Secondary school: 100 000 VND / month
- High school: 120 000 VND / month
This number was applied during the 2016-2017 school year. And the authority is considering exempting the fees for high schools in 2019. Fees for colleges and universities range from VND 5,000,000 to VND 51,000,000/year for the 2017-2018 school year.

Regarding private schools, the tuition fees vary according to each school. For general education, the lowest price could be VND 1 million/month for half-day classes, VND 2 million/month for full-day classes and VND 3 million/month for boarding. In contrast, the highest price could go up to VND 48 million. Students in private schools or international schools usually pay much more than students in public schools. Instead, they are provided with a more modern facility and an environment more open to international concepts.
Summary of the education system in Vietnam
Education in Vietnam has always been considered crucial and is the foundation for future success. Like in many other parts of the world, highly qualified people are highly respected in Vietnam. In recent years, Vietnam has deployed many innovations to update and improve the quality of education. Vietnam’s education system is expected to develop more and more in the future, as it is considered the cornerstone of a prosperous nation.



